Episodios
-
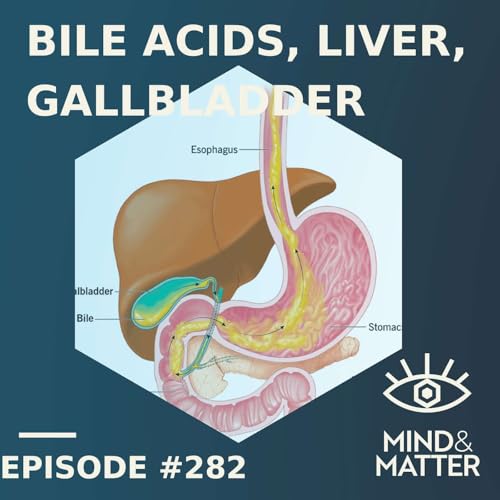 Feb 28 202653 m
Feb 28 202653 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 1 h y 31 m
1 h y 31 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 1 h y 18 m
1 h y 18 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 1 h y 40 m
1 h y 40 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 1 h y 36 m
1 h y 36 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 Feb 5 20261 h y 11 m
Feb 5 20261 h y 11 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 1 h y 20 m
1 h y 20 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente -
 Jan 19 20261 h y 36 m
Jan 19 20261 h y 36 mNo se pudo agregar al carrito
Solo puedes tener X títulos en el carrito para realizar el pago.Add to Cart failed.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al Agregar a Lista de Deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al eliminar de la lista de deseos.
Por favor prueba de nuevo más tardeError al añadir a tu biblioteca
Por favor intenta de nuevoError al seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamenteError al dejar de seguir el podcast
Intenta nuevamente

